



- Main Page
-
Testimonials
Testimonials
History has recorded Muhammad’s sublime and humane dealing with people. His call and teachings were based on amicability and fraternity. Adversity had no place in his conduct.
Read More + -
His character
His character
Muslims have no drawings or pictures for prophet Muhammad or the prophets before him. However, unlike the founders of the great faith traditions prior to his time, the Prophet Muhammad is much more a recognizable historical figure as his companions and family members described him very well and recorded many stories from his life for posterity.
Read More + - Biography
Biography
History has recorded Muhammad’s sublime and humane dealing with people. His call and teachings were based on amicability and fraternity. Adversity had no place in his conduct.
Read More + - Prophecy
- The Islamic civilization
The Islamic civilization
- Women in islam
- Human rights
Human rights
Muhammad proclaimed himself as a Messenger of God. He received a Divine Message to humanity and struggled to convey it to all people but he did not force anyone to accept it.
Read More + - Environment
Environment
The bowing tree was found in a camping site in Nowra, South of Sydney, Australia. It resembles bowing to God in the Muslims' prayers. The lower edge of the tree looks like the head of a bowing person.
Read More + - The Miracles
- His sayings
- Epilogue
Epilogue
History has recorded fine details of Muhammad’s life as well as his sublime and humane dealing with people.
Read More + - Islamic Arts
- Latest News

- Home
Biography


MUHAMMAD
Biography
Personal Details

| Name | |
Muhammad |
|---|---|
| Father’s Name | |
Abdullah, son of Abdul-Muttalib (ancestry reaches back to the Prophet Ishmael son of Prophet Abraham) |
| Surname (Clan) |
|
He was from Bani-Hashim family (Bani-Hashim was from Quraysh, a tribe that was highly ranked in Arabia) |
| Date of Birth | |
20th - 22nd April, 570 CE 1 Approximately |
| Place of Birth | |
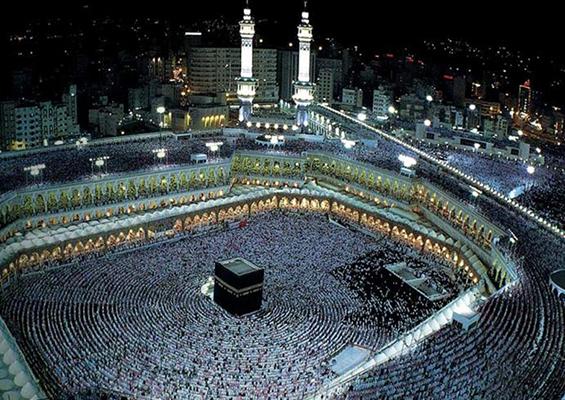
City of Mecca (Makkah) – Arabian Peninsula (currently in Saudi Arabia) |
| Date of Death | |
6th June, 632 CE. (Approximately, he was 63 years old when he passed away) |
| Death & Burial Place |
|
City of Madinah (about 400 km north of Makkah) |
Childhood & Adolescence

| Birth - 2 years old | |
Muhammad had no brothers or sisters. His father passed away before he was born. His mother sent him out of Makkah to be breast-fed by a wet nurse called Halima (this was an old Arab custom) |
|---|---|
| 2-6 years old | |
He lived with his mother "Aaminah" until she passed away in the year 576 CE. |
| 6-8 years old (Clan) |
|
He lived with his grandfather Abdul-Muttalib until he passed away. |
| 8-25 years old | |
He lived with his paternal uncle (Abu-Talib), who had 10 children. |
Working Life

| Childhood – mid twenties | |
He worked as a shepherd for some time (looking after sheep and goats for others). In addition, he worked in trading with his uncle Abu-Talib. According to authentic narrations, Muhammad was 12 years old when he, for the first time, joined his uncle Abu-Talib in a trading trip to Syria. |
|---|---|
| Mid twenties - 40 years old | |
He worked as a merchant or a trader for a wealthy woman called Khadijah, who had a general trading business (they used to buy commodities from one area and sell them in another). |
| 40-63 years old (Clan) |
|
When he was 40 years old (year 610 CE) Muhammad received the divine revelation and dedicated his life to conveying God’s Message to all people. He taught people the oneness of God and conveyed God’s Book (The Quran), which calls for social justice, peace, harmony and wellbeing. |
Education

He could not read or write. He never lived outside Makkah or sought foreign knowledge. Muslims believe that Muhammad¤ did not write or author the “Quran”. He conveyed it (as Allah's Message to humanity) letter by letter and word by word without rephrasing any part of it with his own words.
Muhammad’s sayings and teachings were not mixed with the Quran:
They were collected in books which are called “Hadith or the Sunnah of the Prophet”, which means his teachings, way of life and explanation of the Book (The Quran).
Marital Status

Married to one wife for 25 years:
Muhammad married Khadijah, the daughter of Khuwaylid, who came from a noble family called Asad.
She was a respected woman in her community and she was a widow. Muhammad worked for her for two years before she proposed marriage to him through a third party. She found him a very loyal, transparent and an ethical person.
Successful marriage:
Although Khadijah was 15 years older than Muhammad, both of them came from a similar social class in the community.
The age difference was no obstacle to the establishment of a successful marriage, which lasted for 25 years3 until Khadijah died in the year 619 CE at the age of 65. Muhammad remarried after Khadijah passed away. (Please see Chapter 6)
A father of 6 children and a family man:
Muhammad & Khadijah lived in harmony and peace; they had four daughters (Zaynab, Ruqayya, Um Kulthoum & Fatima) and two sons (AlQasim, who died when he was 3 years old and Abdullah, who died at the age of 4). Muhammad used to spend time with his family, help his wife in house matters, sew his own clothes and look after his children.
610 evt.

Divine revelation commenced:
Muhammad received the first revelation from God and was appointed as the Messenger of God to all people. A mission that required strong belief, dedication, commitment and honesty.
610 - 612 CE

Core Muslims formed:
Muhammad invited his friends, his inner circle and selected people to believe in one God and accept Islam as His final Message to humanity. In the first three years after prophecy, around 130 people accepted Islam and became a strong nucleus that was able to spread Islam publicly. These core Muslims were a mix of rich and poor people.
613 - 615 CE

Muhammad’s public invitation resisted:
Muhammad and his followers started to talk to people openly about Islam. Although Muhammad was known as a trustworthy and an honest man, Meccan leaders did not believe him. They described him as a poet, a magician and a crazy man.
Muhammad tempted and threatened:
Meccan leaders tried to dissuade Muhammad from inviting people to Islam by tempting him one time and threatening him another time.
Also, they tried to prevent people from listening to him. They showed increased hostility towards new Muslims. They persecuted and tortured the poor and weak Muslims.
Muhammad supported his followers and sent some of them to Abyssinia:
Muhammad was very close to his followers. He used to meet them at Al-Arqam House which was like a small college. He taught them values and morals and instilled feelings of responsibility and commitment. Muhammad saw the suffering and tribulation some of his followers endured and advised them to seek refuge in Abyssinia, describing it as a land of virtue ruled by a fair Christian king, under whom no one was treated unjustly.
Two influential men embraced Islam:
Two strong and well respected Meccan men accepted Islam, Omar Bin AlKhattab and Hamza Bin Abdul-Muttalib (Muhammad’s uncle). That was an important turning point for Muslims. Hamza became a strong supporter and protector for Muhammad until he (Hamza) died in the battle of Uhud (625 CE). Three years after the passing away of Prophet Muhammad, Omar became the second caliph and ruled the Islamic state for 11 years.
616 - 618 CE

Muhammad boycotted :
Meccan leaders boycotted Muhammad and his followers and imposed a social and economic blockade on them, which lasted for 3 years. During this time, Muhammad and his followers suffered great tribulation. This period was a tough test for their patience, belief and commitment to the truth.
619 - 620 CE

A Sorrowful year:
Meccan chiefs cancelled the social and economic blockade as they found it not useful. In the same year, Muhammad’s wife Khadijah and his uncle Abu-Talib passed away. Muhammad lost hope in Makkah and decided to convey the Message of God and seek support outside Makkah. He went to the city of Ta'if but was met with hostility4. In addition, he spoke to more than 20 Arab tribes about Islam but he didn’t receive any positive response.
620 - 622 CE

A glimpse of hope :
Muhammad met six people from Yathrib (a city located 400 km north of Makkah) during the pilgrimage time and talked to them about Islam. They believed Muhammad and returned to their city with intentions to invite more people from their own tribe and other tribes in Yathrib. They agreed to return to Makkah the next year at the time of pilgrimage to meet again with Muhammad “the Prophet and the Messenger of God”.
New Muslims pledged allegiance to Muhammad:
The same group returned the following year (621 CE) with six more people. They pledged their allegiance to Muhammad (accepting him as the Messenger of God.
They promised him:
1- not to worship anyone except Allah
2- not to steal
3- not to commit adultery
4- not to kill
5- not to slander neighbors and
6- not to disobey the Messenger of God.
The group went back to Yathrib and invited their tribal leaders and their people to accept Islam. They returned again in the following year (622 CE) at the time of pilgrimage with more than 70 men and two women. A similar pledge of allegiance was given by this group to Prophet Muhammad.
A new Muslim community formed 400 km north of Makkah: The leaders of the two main tribes in Yathrib (Aws & Khazraj) embraced Islam and subsequently their people became Muslims. Muhammad the Prophet of God was invited to come to Yathrib and become its ruler and leader.
622 CE

Chiefs of Makkah plotted to kill Muhammad; migration to Yathrib commenced :
Things were becoming worse in Makkah. Muhammad asked Meccan Muslims6 to migrate to Yathrib. Following their migration, Muhammad migrated to Yathrib in September 622 CE7 . His migration represented the most important turning point in the Islamic history. From Yathrib, Islam blossomed, an Islamic state was established and a just social order was born.
623-624 CE

Muhammad the ruler of Yathrib:
Muhammad the ruler of Yathrib Muhammad, “The Messenger of God” became the ruler of Yathrib willingly and peacefully with the agreement of the majority of people. The people of Yathrib were a mix of Arabs and Jews. Although there were two main Arab tribes and three smaller Jewish tribes, the Arab community was larger than the Jewish one.
Muhammad changed the name of Yathrib the multicultural society :
“Madinah” was the new name Muhammad gave to the city of Yathrib.
After the migration of the Meccan Muslims, Yathrib no longer belonged to a certain group of Arabs, instead, it became the homeland of believers who accepted Islam.
Since there were Jewish tribes in Yathrib and other Arab people who didn't embrace Islam, Muhammad did not call it the city of Islam. Instead, it was named “Al-Madinah” which means “The City”, in which all inhabitants had similar citizenship rights.
Muhammad called for peace and unity in Madinah:
In his first public address to the people of Madinah, Muhammad delivered a very concise speech which promoted harmony and social cohesion. He said:
“O People, seek and spread peace and offer food to each other, look after your kinship and pray to God at night while others are sleeping so you gain God’s pleasure and enter His Paradise”.
Muhammad linked these acts to God’s pleasure in order to motivate people to love each other and live in peace and harmony in a multicultural society.
623 - 624 CE

Muhammad signed the first agreement with Jews in Madinah which protected human rights and liberties:
Most of the Jews hoped that the last Prophet would come from a Jewish background. Although the majority of Jews did not accept Muhammad as a Messenger of God, Muhammad (as the ruler of the state) signed an agreement with them which was like a “Constitution and Charter of Human Rights and Liberties” to which all Arab and Jewish tribes agreed upon.
The agreement guaranteed the freedom of worship for Muslims and Jews as well as Arabs who did not accept Islam. In addition, the agreement protected the safety and security of all citizens in Madinah and required all parties to be part of the national defense should Madinah be attacked by enemies. The agreement stated justice, human rights, liberties and prohibition of crime and immoral practices.
624 CE
The unavoidable battle of Badr:
When Muslims migrated from Makkah to Madinah, many of them were forced to abandon their homes and their properties were confiscated.
The chiefs of Makkah used the confiscated money in trade and business. Muslims knew about a trade caravan belonging to the Meccan chiefs, led by their enemy AbuSufyan, which would pass through a trade route close to Madinah.
Muhammad called upon Muslims to take the caravan in return for their wealth that was confiscated in Makkah. A force of only 313 Muslims took up the mission. The Meccan intelligence advised Abu-Sufyan to change the route of the trade caravan. In addition, Makkah sent an army of 950 soldiers to fight the Muslim force, which was not prepared for war and was far less equipped than the Meccan army.
It was astonishing and beyond expectation that Muslims won their first battle against the Meccan chiefs. Many Meccan chiefs and important figures were killed in this battle.
625 CE
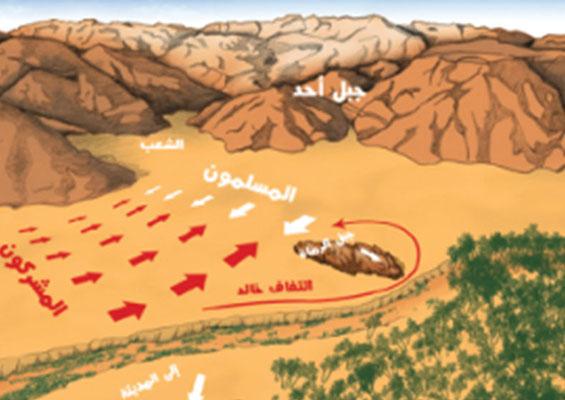
Meccan chiefs attacked Muhammad and his followers in the battle of Uhud:
In retaliation for their loss in the battle of Badr and their fear of losing their leading role in Arabia, Meccan chiefs with some Arab allies, sent an army of 3000 soldiers to at the mount of Uhud north of Madinah. The Muslims lost this battle and Muhammad was wounded but saved. In the battle of Uhud some of Muhammad’s companions were killed including his beloved uncle Hamza.
The Muslims lost this battle and Muhammad was wounded but saved. In the battle of Uhud some of Muhammad’s companions were killed including his beloved uncle Hamza.
626 CE

Meccans and other tribes attacked Muhammad and his followers in the battle of trench:
This battle is also called the “Battle of Confederates”. Since Muhammad was not killed in the previous battle, Meccan chiefs and some Arab & Jewish tribes called for a united effort and a comprehensive assault to kill Muhammad and destroy the Muslim community.
10,000 soldiers marched towards Madinah. After consulting his companions, Muhammad decided to adopt the proposal of a Persian Muslim named Salman to dig a trench on the northern access of Madinah (5.5 km long X 4.6 m wide).
Muslims were in their most awkward situation and tried their best including psychological warfare to defend themselves. After a month-long siege the Meccan army and its allies became impatient and strong storms and wind blew, which forced the confederates to pack up their tents and withdraw.
627 CE

Treaty of Hudaybiya, a truce for 10 years:
One year after the battle of trench, Muhammad took a peaceful initiative to perform Umrah (visit the Sacred Mosque in Makkah and perform other religious rites). Visiting Makkah for the purpose of worship was a religious right that Makkah undertook to give to all people in Arabia.
It was a great surprise for Meccan chiefs to see Muhammad approaching Makkah with 1400 civilians coming from Madinah.
After several negotiations, a truce was made between the Meccan chiefs and Muhammad for 10 years during which time Muhammad and his companions returned to their homes with a condition to come again to visit Makkah in the following year (628 CE). The truce had many other terms which were disappointing for Muslims because they weighed heavily in favor of the Meccan side.
628 - 629 CE

During the truce, Muhammad conveyed God’s Message inside & outside Arabia:
The truce was a golden chance for Muhammad to freely speak to people about Islam without being stopped or intercepted by other forces.
Muhammad sent delegations to other Arab tribes in Arabia and wrote letters to the rulers and kings of neighboring countries and superpowers such as Persia, Byzantine and Egypt inviting them to accept Islam as “the Message of God”. Muslims increased in numbers as people found the truth in Islam.
630 CE

Peaceful take-over of Makkah:
Within less than 2 years, the truce was broken from the Meccan side when their allies killed 20 Muslims.
In response to this shocking act, Muhammad marched with 10,000 Muslims to conquer Makkah but asked his soldiers not to fight any one unless they were fought.7
The Meccan chiefs were embarrassed and were not prepared to fight the Muslims. When the Muslim army arrived in Makkah, Muhammad addressed the whole people of Makkah confirming the oneness of God, referring victory to Him and reminding people that all of them descended from Adam and Adam was created from dust of the ground.
Then he asked the people of Makkah: “What do you expect me to do with you? They replied: “We hope for the best. After all, you have been a gracious brother and a courteous cousin”.
Exemplar of forgiveness :
Despite the hardship caused by the Meccan people during the previous 21 years, Muhammad behaved with high moralities. He replied: “Have no fear today. Depart then (to your homes), you are free”. Muhammad’s address was very influential and many people came to him to make a pledge and embrace Islam. (Sunan Al-Bayhaqi, 9/118, 18342, 18343)
630 - 631 CE

Arab tribes embraced Islam:
After the peaceful takeover of Makkah, delegations from all over Arabia came to learn about Islam. Except the Hawazen tribe, who fought the Muslims and eventually lost the battle of Hunayn, most Arab tribes embraced Islam. Muhammad sent many of his companions to various provinces in Arabia to teach people Islam “The Message of God”.
" When Prophet Muhammad returned to Makkah, his main goal was to purify the Sacred Mosque. He knocked down all idols that were worshipped by the Arabs and restored the Ka'bah as the House of Allah, the One God"
632 CE

Muhammad's farewell address:
Muhammad’s mission was accomplished and his life was nearing to an end. In the year 632 CE Muhammad performed pilgrimage and gave his final sermon to more than 100,000 people.
His sermon reminded people about belief in One God, sanctity of lives, protection of wealth and property, equality of all races, rules of justice, women’s rights and morals.
The passing away of Muhammad:
Prophet Muhammad passed away in his home in Madinah in the year 632 CE leaving only few possessions. He did not leave any money or wealth but a legacy of faith in God that is still illuminating the hearts of millions of people around the globe.
"To err is human, to forgive is Divine" Alexander Pope